Busan Rises to 13th in Global Smart Centres Index
Busan, South Korea - Busan has solidified its position as a global leader in innovation, technology, and business competitiveness by achieving 13th place in the 10th edition of the Smart Centres Index (SCI), a report published by the Z/Yen Group. The report evaluates the technological and economic competitiveness of 77 cities worldwide. Busan also emerged as Asia’s second-ranked city, trailing only Singapore, while surpassing Hong Kong and Seoul, reinforcing its status as a key player in the region.
The Smart Centers Index measures cities based on three dimensions: Innovation Support, Creative Intensity, and Delivery Capability. Since its first inclusion in SCI rankings in 2021 (62nd place), Busan has consistently climbed the ranks, becoming the only city to achieve sustained progress over consecutive editions. From 62nd to 13th in just over three years, Busan’s leap of 49 places highlights its commitment to building a digitally empowered economy.
Mayor Park Heong-joon celebrated the achievement, noting that the city’s rise “underscores its reputation as a digital transformation leader” and serves as a testament to the city’s ambitious policies focused on innovation, infrastructure, and business development.
Busan's impressive performance in the Smart Centres Index (SCI) is built upon a foundation of notable strengths across several key categories. The city's business environment stands out, securing a remarkable 6th place globally. This ranking highlights Busan's effective regulatory frameworks and robust support for corporate operations, creating a fertile ground for innovation and economic activity.
The city’s reputation also shines, ranking 8th globally. This reflects its growing appeal among global experts and industry leaders, who recognize Busan’s potential as a hub for cutting-edge technology and innovation.
In the realm of human capital, Busan has made significant strides, achieving 8th place. This underscores the city's ongoing efforts to cultivate a highly skilled workforce, capable of driving forward technological advancements and supporting the demands of a rapidly evolving economy.
Additionally, Busan’s investment in infrastructure has paid off, earning the city a 10th-place ranking. By developing state-of-the-art digital and physical infrastructure, Busan has laid the groundwork to sustain its transformation into a leading smart city. These strategic investments ensure the city is well-equipped to meet future challenges while continuing to attract global attention and investment.
Busan's Rankings and Indicators in the Smart Centres Index (SCI) 10
| Evaluation Category | Global Rank | Description | Key Indicators | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Environment | 6th | Excellence in regulatory frameworks and business-friendly environment | - Government Efficiency (World Bank) - Economic Freedom Index (Fraser Institute) - Rule of Law Index (World Bank) | World Bank, Fraser Institute |
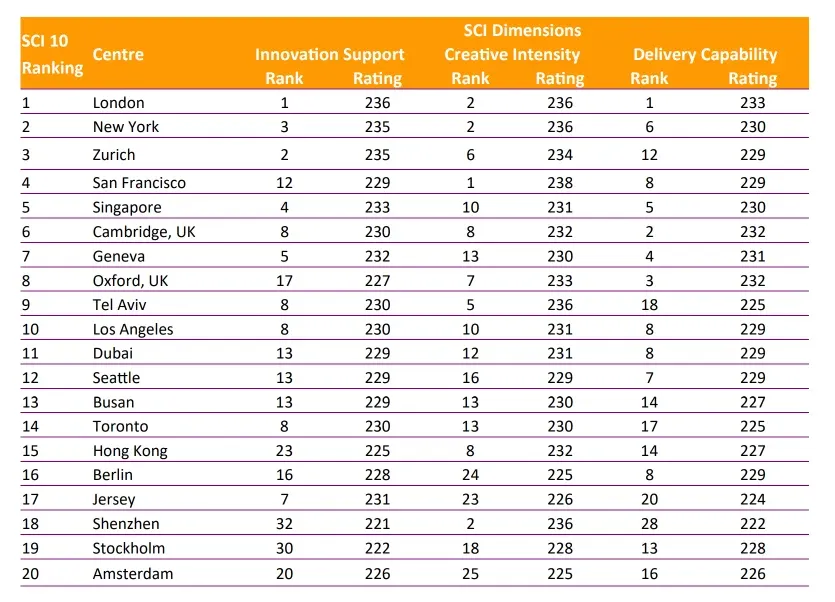
| Reputation | 8th | Strong reputation among global experts and industry leaders | - Global Competitiveness Score (IMD) - Global Power City Index (Mori Memorial Foundation) - Innovation Cities Index (2ThinkNow) | IMD, 2ThinkNow |
| Human Capital | 8th | Skilled workforce development and human resource capabilities | - Human Development Index (UNDP) - World Talent Ranking (IMD) - Human Freedom Index (Cato Institute) | UNDP, IMD, Cato Institute |
| Financial Services | 8th | Strengths in financial ecosystems and support | - Global Financial Centres Index (Z/Yen) - Global Green Finance Index (World Wide) - Stock Market Trading Value (World Federation of Exchanges) | Z/Yen, World Bank |
| Infrastructure | 10th | Investments in digital and physical infrastructure | - Global Sustainable Competitiveness Index (Solability) - Logistics Performance Index (World Bank) - Energy Transition Index (World Economic Forum) | Solability, World Bank |
| Technology | 14th | Capabilities in technological innovation and digital transformation | - Global AI Index (Tortoise Intelligence) - Smart City Index (IMD) - Global Fintech Index (Findexable) - Bitcoin Trading Volume (Coin Dance) | Tortoise, IMD |
| Delivery Capability | 14th | Effectiveness in implementing innovations and achieving tangible outcomes | - Metrics related to commercialization pipelines, adoption of emerging technologies, and real-world application of innovations |
Busan’s rise to Asia’s second spot is particularly noteworthy as it surpasses Hong Kong (15th), a long-standing hub of technological innovation, and maintains its lead over Seoul (30th). Yet, a closer look at the SCI report reveals areas for improvement and highlights potential overstatements in Busan’s official narrative.
While Busan achieved high rankings in innovation support and business environment, its Delivery Capability (14th) indicates a relative weakness in executing and commercializing innovations. Cities like Singapore (5th) and Shenzhen (18th) have demonstrated stronger results in applying technological advancements to industries. Addressing this gap will be crucial for Busan to sustain its upward trajectory.
Busan’s Creative Intensity (13th) lags behind cities such as Hong Kong (8th) and Shenzhen (2nd). This metric reflects the extent to which technology is embedded within a city’s economy. While Busan has made significant progress, fostering deeper integration of emerging technologies such as AI, fintech, and renewable energy solutions will be vital to compete with leading global tech hubs.
Despite facing certain challenges, Busan is strategically poised to build on its current momentum and further establish itself as a global smart city. Key initiatives such as the establishment of the Digital Economy Bureau and the One-Stop Corporate Support Centre have played a pivotal role in simplifying regulatory processes and fostering stronger corporate engagement. These efforts, coupled with significant investments in advanced industries like artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and renewable energy, reflect Busan’s unwavering commitment to sustainable, long-term growth.
To maintain its competitive edge and solidify its global standing, Busan must prioritize several key areas. First, it needs to enhance its delivery capability, ensuring that innovations are effectively applied across industries and supported by robust commercialization pipelines. This will help bridge the gap between technological potential and practical implementation.
Second, the city must focus on deepening technology integration by nurturing a vibrant tech ecosystem. This can be achieved through strategic partnerships, startup incubators, and increased investment in research and development (R&D). By fostering collaboration between stakeholders, Busan can accelerate innovation and cement its role as a hub for emerging technologies.
Third, it is essential to balance perception with reality. While Busan has earned a strong global reputation, delivering tangible results in areas like smart infrastructure and workforce development will be critical to sustaining its credibility and attracting further investment.
Finally, Busan should expand its efforts in global collaboration by learning from leading cities like Singapore and Shenzhen. Forming international alliances and attracting global talent and resources will not only bolster Busan’s competitive edge but also elevate its status as a global hub for innovation and technology. Through these strategic initiatives, Busan can continue its remarkable trajectory and secure its place among the world’s most advanced smart cities.
Busan’s rise to the 13th spot in the SCI 10 is a significant milestone, reflecting its commitment to innovation and digital transformation. However, realizing its ambition to become a true global technology hub requires addressing challenges in execution and technology integration. By focusing on sustainable growth strategies and leveraging its reputation, Busan can continue to climb the ranks and establish itself as a leader among the world’s smartest cities.
- Strengths:
- Business Environment (6th).
- Reputation (8th).
- Human Capital (8th).
- Financial Services (8th).
- Improvement Areas:
- Technology (14th).
- Delivery Capability (14th): Indicates the need to strengthen execution strategies and innovation commercialization.



Comments ()